The title suggests that the living cells found in labs come from trusted sources. These cells are key in scientific progress, especially in medicine and biotech. They help researchers study how cells work and create new treatments.
They come from different places like humans, animals, and microbes. This shows how important they are in today’s labs.
We will explain where lab-grown cells come from, what types there are, and how they’re used. We’ll highlight their role in today’s science.
Key Takeaways
- Easily attainable living cells have diverse origins crucial for research.
- Cell observation aids in understanding complex biological processes.
- Lab-grown cells are pivotal in therapeutic developments.
- Sources include human, animal, and microbial cell lines.
- Understanding these cells facilitates advancements in biotechnology.
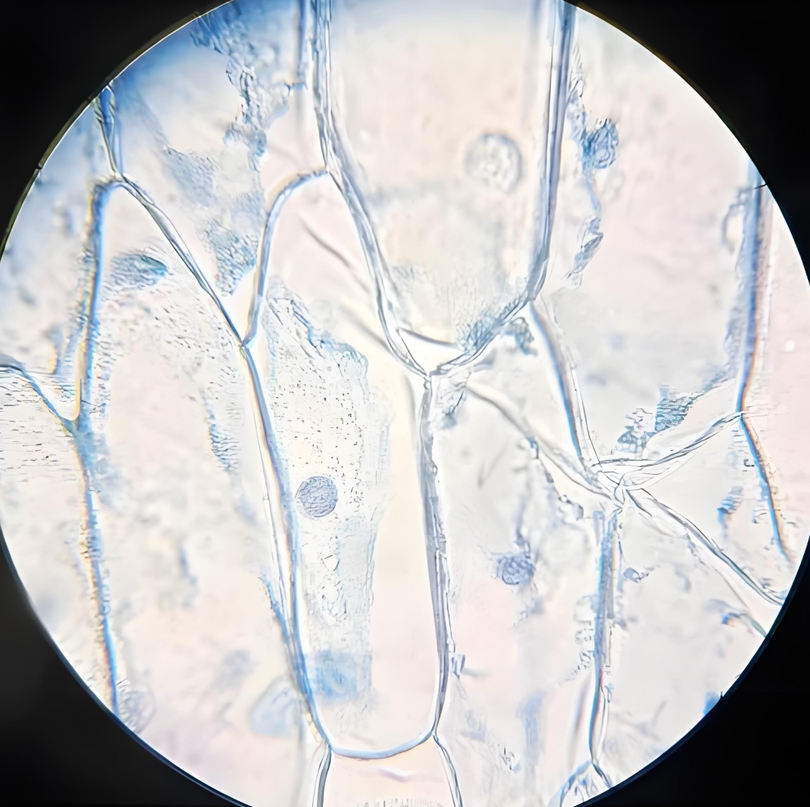
Understanding Living Cells in Laboratory Settings
Living cells are the heart of life in labs. They have a special structure, work through metabolism, and can make copies of themselves. Scientists use cell culture techniques to study these cells. This helps them understand life and diseases better.
Definition and Characteristics of Living Cells
Living cells are the basic parts of all life. They have unique features like:
- Cellular structure: Organelles help cells work.
- Metabolism: Cells make energy through chemical reactions.
- Replication: Cells can make copies, allowing for study.
Importance of Studying Living Cells
Studying living cells is key for many reasons:
- It helps create new treatments for diseases.
- It sheds light on complex biological processes.
- It boosts laboratory cell analysis skills.
Common Types of Living Cells Used in Labs
Scientists often use different types of cells in labs, such as:
| Type of Cell | Source | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Human Cells | Derived from tissues | Drug testing, disease modeling |
| Animal Cells | Obtained from different species | Vaccine development, genetic studies |
| Microbial Cells | Bacteria and yeast | Biotechnology, food production |
Sources of Easily Attainable Living Cells
Learning about the origins of living cells helps us in many scientific areas. They are key for research, making new products, and finding new treatments. We’ll look at where we get human cell lines, animal cell cultures, and a brief on bacterial and fungal cells.
Human Cell Lines: Origins and Applications
Human cell lines come from human tissues. They are vital for studying drugs and cancer. They let us study diseases and test treatments without harming people.
Cells like HeLa and A549 are very important. They help us understand cancer and find new treatments.
Animal Cell Cultures: Varieties and Uses
Animal cell cultures are used in many ways, like making vaccines and testing toxins. They come from animals and give us insights into biology. Cells like CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) are used a lot in making medicines.
They help make sure medicines are safe before they’re tested on people.
Bacterial and Fungal Cells: A Quick Overview
Bacterial and fungal cells are important in studying microbes and biotechnology. They help in genetic engineering, making proteins and enzymes. They grow fast and are easy to work with.
Knowing about these cells opens up new ways to solve problems in medicine and industry.
Techniques for Cultivating Living Cells
Learning about different cell culture methods is key for biology and medicine research. These techniques help grow living cells in a controlled way. This lets researchers study how cells behave. We’ll look at cell culture methods, the benefits of in vitro techniques, and the importance of safety and ethics.
Cell Culture Methods Explained
There are two main cell culture types: adherent and suspension cultures. Adherent cultures need cells to stick to a surface, like a petri dish. Suspension cultures let cells float in a liquid. Both are important for studying how cells live and behave.
| Cell Culture Method | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Adherent Culture | Cells grow attached to a surface. | Studies on cell morphology and interactions. |
| Suspension Culture | Cells grow suspended in liquid media. | Large-scale production of cells and proteins. |
Advantages of In Vitro Techniques
In vitro techniques offer great control over conditions like temperature and nutrients. This control helps mimic the real body environment while focusing on specific factors. It makes experiments more consistent and reliable.
Safety and Ethical Considerations in Cell Culturing
Keeping cell cultures safe is crucial. Labs must follow rules for handling cells and disposing of waste. They also need to prevent contamination. Ethical rules include getting consent for human cells and using animal cells responsibly. Following these rules helps research grow in a responsible way.
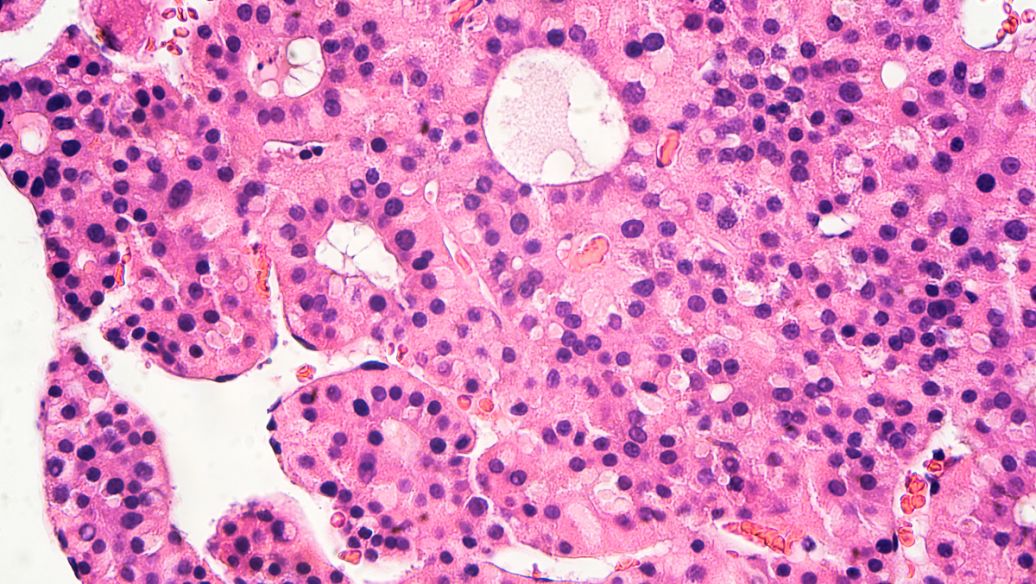
Popular Living Cell Models in Research
In the world of cellular studies, many living cell models are key for scientific progress. HeLa cells, CHO cells, and stem cells are among the most important. Each type has special traits that make them crucial for different research areas.
HeLa Cells: The Pioneer of Cell Lines
HeLa cells come from cervical cancer and are the first immortal human cell line. They are very stable and live well in labs, helping a lot in cancer research and testing drugs. Because of this, they are studied all over the world.
CHO Cells: Versatility in Biopharmaceuticals
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are vital in the biopharmaceutical field. They can make complex proteins for medicine very well. CHO cells are often used to make monoclonal antibodies and proteins, helping to treat many diseases.
Stem Cells: The Future of Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells are at the forefront of research, with big hopes for regenerative medicine. They can turn into many different cell types, making them key for new treatments. Research on stem cells could lead to cures for diseases that were once thought impossible.

leukocyte
Applications of Living Cells in Science
Living cells are key in many scientific areas, leading to new discoveries. They help in making new medicines and testing their safety. They also aid in genetic engineering. This shows how important they are in science and medicine.
Developing New Therapies and Drugs
Living cells are crucial for finding and making new treatments. They help scientists quickly test new medicines. This way, they can find out if a drug works well and is safe.
Cell-based tests let scientists see how cells react. This helps in finding new ways to treat diseases. It opens up new possibilities for treating illnesses.
Toxicology and Safety Testing
Toxicology tests use living cells to check if new substances are safe. By using cell cultures, scientists can see how substances affect cells. This helps in understanding how much of a substance is safe to use.
This method is important for making sure products are safe for people. It helps in reducing health risks. It ensures that products are safe for everyone to use.
Advancements in Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering has made big strides with living cells. Tools like CRISPR let scientists edit genes with great precision. This could help solve genetic problems.
Using living cells in labs helps in making gene therapies better. It shows how cell biology can tackle tough medical issues. It’s a big step forward in treating genetic diseases.
| Application | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| New Therapies | Identification and development of pharmaceutical candidates | Increased treatment options |
| Toxicology Testing | Assessing safety and biological impact of chemicals | Ensured consumer safety |
| Genetic Engineering | Gene editing for disease treatment | Potential cures for genetic disorders |
Comparative Analysis of Cell Types
It’s important to know the differences between different cell types for science. This part talks about the differences between human and animal cells. It also looks at the differences between bacterial and eukaryotic cells. We also think about how much it costs to use each type of cell in research.
Human vs. Animal Cells: Key Differences
Human and animal cells are different in many ways. This affects how they are used in labs:
- Cell Structure: Human cells have more complex structures. Animal cells can vary by species.
- Genetic Material: Human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Animal cells have different numbers.
- Applications: Human cells are used in drug testing and disease research. Animal cells are used in vaccine production and other studies.
Bacteria vs. Eukaryotic Cells: A Contrast
The differences between bacterial and eukaryotic cells affect how research is done:
- Cell Type: Bacterial cells are prokaryotic, without a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles.
- Replication: Bacteria reproduce by binary fission. Eukaryotic cells often use mitosis.
- Research Applications: Bacterial cells are key in microbiology studies. Eukaryotic cells are important in genetics and cell biology.
Cost-Effectiveness in Cell Type Selection
When choosing cell types for research, cost is important. Here are some points to think about:
- Human cells need expensive growth factors and special environments. This can increase research costs.
- Animal cells might be cheaper. But, the type of animal and the application can raise costs.
- Bacterial cells are often cheaper in time and resources. They are a popular choice for many experiments.
Future Trends in Cell Research
Looking ahead, cell research will see many changes. New ways to grow cells will help us understand how they work. These methods are key to making research more accurate.
Innovations in Cell Culturing Techniques
New cell culturing methods, like 3D systems and bioreactors, are on the horizon. They aim to mimic real-life conditions for cells. This means better data for scientists.
Materials science is also advancing. It’s creating materials that help cells grow and change. These materials are crucial for cell research.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cell Research
Artificial intelligence is now a big part of cell research. AI can quickly analyze huge amounts of data. It finds patterns that humans might miss.
AI also helps in making cell cultures better. It predicts how cells will react to treatments. This makes experiments more efficient.
Ethical Considerations Moving Forward
With these new tools, we face important ethical questions. Researchers must use cell lines wisely. They must think about the broader impact of their work.
It’s vital to balance innovation with ethics. This way, cell research can grow responsibly. It must consider the future of our planet and society.
Challenges in Working with Living Cells
Working with living cells comes with many challenges. One big issue is contamination. It can ruin cell cultures. To avoid this, researchers need strict protocols and a clean environment.
Contamination Issues in Cell Cultures
Contamination can come from bacteria, fungi, or mixing different cell lines. It can mess up results, wasting time and money. Labs must have good ways to spot and deal with contamination.
Financial Implications of Cell Research
Funding is key in cell research. It limits what projects can do. Researchers must be smart with money to keep their work going.
Regulatory Hurdles in Cell-Based Studies
Following rules is crucial in cell research. There are strict guidelines for working with cells. Knowing these rules helps plan and do projects well.
Conclusion: The Importance of Living Cell Research
Exploring living cells is key to many groundbreaking scientific studies. We learn a lot from human cell lines, animal cultures, and microbes. This knowledge helps a lot in medicine, biotech, and farming.
These cells help us find new ways to treat diseases and make medicines. They also aid in research, showing how vital cell technology is today.
Looking at cell research, we see it’s vital for progress. It has led to big steps in regenerative medicine and tailored treatments. It’s important for scientists to think about ethics as they work.
This work helps us understand biology better and improves health worldwide. It also helps the planet.
The future of cell tech depends on teamwork and deep research. By focusing on cell research and solving new problems, we lead in science. We’re ready to tackle big medical and environmental challenges ahead.
References and further readings:
1.Luisi, P. L. (2002). Toward the engineering of minimal living cells. The Anatomical Record, 268(3), 208–214.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ar.10155
2.Chowdhuri, S., Cole, C. M., & Devaraj, N. K. (2016). Encapsulation of living cells within giant phospholipid liposomes formed by the inverse-emulsion technique. ChemBioChem, 17(4), 392–395.
https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbic.201500643
3.Stuhrmann, B., Jahnke, H. G., Schmidt, M., & Jähn, K. (2006). Versatile optical manipulation system for inspection, laser processing, and isolation of individual living cells. Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(6), 063116.
https://pubs.aip.org/aip/rsi/article-abstract/77/6/064904/354758/Determination-of-thermal-conductivity-distribution?redirectedFrom=fulltext
FAQ
What are easily attainable living cells observed in the lab from?
Living cells in labs come from humans, animals, bacteria, and fungi. These cells help in many research areas, like medicine and biotech.
What defines a living cell?
Living cells have a structure, work through metabolism, and can make copies of themselves. These traits help us learn about life and find new treatments.
Why is studying living cells important?
Studying cells helps us grow scientific knowledge, especially in medicine, genetics, and toxicology. It’s key for creating new treatments and understanding how cells work.
What types of living cells are commonly used in laboratories?
Labs use human, animal, and microbial cells. Each type is used for different research goals and has special qualities.
What are the main sources of human cell lines in research?
Human cells come from tissue biopsies or cell cultures. They’re vital for studying drugs and finding new treatments, acting as good models for experiments.
How are animal cell cultures utilized in scientific research?
Animal cells help make vaccines and test toxicity. They’re a good choice instead of using whole animals, important in early research stages.
What role do bacterial and fungal cells play in laboratory settings?
Bacteria and fungi are used in genetic engineering and biotech. They help test cell health and make compounds for industry use.
What are the advantages of in vitro cell culture techniques?
In vitro methods let researchers control conditions closely. This helps them watch cell behavior and health, making experiments more precise.
What are HeLa cells and why are they important in research?
HeLa cells are immortal cells from cervical cancer. They’re crucial in medical studies, especially in cancer and drug development.
How are CHO cells utilized in the biopharmaceutical industry?
CHO cells are used for making therapeutic proteins. They’re key in creating biological drugs and vaccines.
What emerging trends are shaping the future of cell research?
New trends include 3D cultures and AI for data. These advancements help us understand cells better and improve research results.
What challenges do researchers face when working with living cells?
Researchers face issues like contamination, budget limits, and following ethical rules. These challenges make their work harder.
Leo Bios
Hello, I’m Leo Bios. As an assistant lecturer, I teach cellular and
molecular biology to undergraduates at a regional US Midwest university. I started as a research tech in
a biotech startup over a decade ago, working on molecular diagnostic tools. This practical experience
fuels my teaching and writing, keeping me engaged in biology’s evolution.








Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *