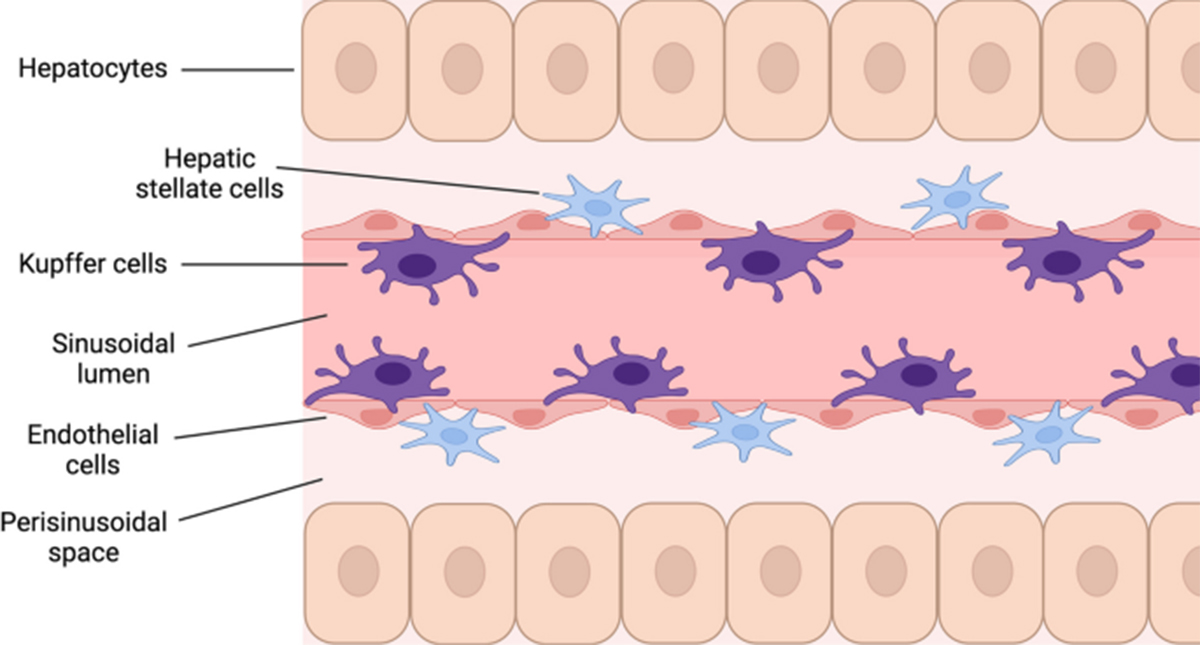
(Image Source:Graham, C.T., Gordon, S. & Kubes, P)
Hepatic macrophages (HMs), also known as Kupffer cells, are phagocytic cells that play an important role in many hepatic disorders due to their ability to respond to a variety of stimuli and activating signals. Here, we provide a detailed protocol to isolate hepatic macrophages from human liver.
Materials and Reagents
1. Collagenase II (sigma C6885): prepare a stock concentration of 50 mg/mL in RPMI media (i.e., dissolve 0.5 g in 50 mL of RPMI media), filter through a 0.22 μm filter and make aliquot of 500 μL. Store aliquots at -20 ℃.
2. DNase I (Roche 10,104,159,001): prepare a stock concentration of 10 mg/mL in RPMI media, filter through a 0.22 μm filter, and make aliquots of 500 μL. Store aliquots at -20 ℃.
3. Media: Sterile RPMI media (ThermoFisher cat # 21875034).
4. Sterile complete media (RPMI media +10% FCS + 0.5%pen/strep).
5. 90% Percoll: For a final volume of 50 mL, add 5 mL of 10×PBS to 45 mL of Percoll (GE Healthcare cat # 15-0891-01).
6. 25% Percoll: For a final volume of 40 mL, add 30 mL of 1×PBS to 10 mL of 90% Percoll.
7. 50% Percoll: For a final volume 30 mL, add 15 mL of 1×PBS to 15 mL of 90% Percoll.
8. Percoll gradient: In a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 20 mL of 25% Percoll and underlay slowly 14.5 mL of 50% Percoll, at the bottom of the tube using a 10 mL plastic pipette.
Equipment
1.Sterile scalpel.
2. Refrigerated centrifuge.
3. Cell strainer(Ucallm).
4.Petri dishes (Ucallm).
5. 50 mL centrifuge tubes (Ucallm).
Procedure
A small piece of liver tissue is freshly collected by the surgeon from volunteers obtained by a small needle is inserted through the abdominal skin into the liver to collect a tissue sample. Before staring the procedure, thaw DNase and collagenase on ice, warm up the water bath to 37 ℃, and bring media and PBS to room temperature.
1.Transfer the liver tissue into a petri dish.
2. Cover the tissue with 1 mL (see Note 1) of RPMI media.
3. Cut into smaller pieces (using a scalpel).
4. Transfer the pieces and media into 50 mL tubethen add 1 mL of RPMI media (total media is now 2 mL, see Note 1).
5. Add collagenase: 25 μL/mL (=50 μL for 2 mL total volume) (stock Concentration=10 mg/mL. Final concentration≈0.25 mg/mL).
6. Add DNase 20 μL/mL (=40 μL for 2 mL total volume) Stock concentration=10 mg/mL. Final concentration≈0.2 mg/mL).
7. Transfer the tube into water bath≈37 ℃ for 30 min with fast shaking.
8. Take out of the tube from the water bath and add 10 mL of complete media (containing FBS) to stop the enzymatic digestion.
9. Filter by passing the cell suspension through the cell strainer(100 or 75 μm). Keep the cell suspension on ice.
10. Centrifuge for 3 min at 50×g at 4℃.
11. Keep the supernatant that contains hepatic macrophages that will be used for the Percoll gradient separation.
12. Slowly layer the supernatant on the Percoll gradient with a 10 mL pipette and spin down at 1500×g for 30 min without
13. Carefully collect the middle interphase (white cell ring) and transfer it into a new 50 mL tube.
14. Wash the cells twice by adding PBS up to a final volume of 20 mL and centrifuging at 640×g for 10 min at 4 ℃.
15. Resuspend in RPMI complete media and plate the cells for 30 min. Wash the cells with PBS and add fresh media to remove the nonadherent cells.
16. Harvest the cell for further analysis.
Notes
1.These volumes are calculated based on liver border biopsy (usually taken during abdominal surgery). If the starting material is from a needle biopsy, volumes need to be scaled down.
References
1.Morgantini, C. (2020). Kupffer Cell Isolation from Human Biopsies. In: Aouadi, M., Azzimato, V. (eds) Kupffer Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2164. Humana, New York, NY.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0704-6_2
2. Graham, C.T., Gordon, S. & Kubes, P. A historical perspective of Kupffer cells in the context of infection. Cell Tissue Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-024-03924-4
Manufacturer’s Link
Sigma-Aldrich: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com
Roche: https://www.roche.com
Thermo Fisher Scientific: https://www.thermofisher.com
GE HealthCare: https://www.gehealthcare.com
Disclaimer:
If any infringement is identified, please contact 【info@ucallmlabs.com】for content removal.
Human Primary Cells
The Immune Cell System
Hepatic Cell System
- Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells
- Human Intrahepatic Biliary Epithelial Cells
- Human Hepatocytes
- Human Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Human Hepatic Macrophages
- Human Gallbladder Fibroblasts
- Human Liver-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Neurons Cell System
- Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Brain Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Brain Vascular Adventitial Fibroblasts
- Human Brain Vascular Pericytes
- Human Choroid Plexus Endothelial Cells
- Human Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells
- Human Choroid Plexus Fibroblasts
- Human Meningeal Cells
- Human Leptomeningeal Pericytes
- Human Dural Fibroblasts
- Human Neurons
- Human Cerebellar Granule Cells
- Human Neurons-hippocampal
- Human Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells
- Human Schwann Cells
Skeletal Cell System
- Human Calvarial Osteoblasts
- Human Osteoblasts-femoral
- Human Chondrocytes-articular
- Human Skeletal Muscle Cells
- Human Skeletal Muscle Myoblasts
- Human Synoviocytes
- Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells
- Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Cardiac Cell System
- Human Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells
- Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Aortic Endothelial Cells
- Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Aortic Adventitial Fibroblasts
- Human Cardiac Myocytes
- Human Cardiac Fibroblasts
- Human Ventricular Cardiac Fibroblasts
- Human Pericardial Fibroblasts
Dermal Cell System
- Human Dermal Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Dermal Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
- Human Dermal Blood Endothelial Cells
- Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
- Human Epidermal Melanocytes
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Scalp Fibroblasts-fetal
Adipose Cell System
- Human Adipose Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Preadipocytes
- Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Human Umbilical Cord Cell System
- Primary Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- Human Umbilical Artery Endothelial Cells
- Human Umbilical Vein Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Umbilical Artery Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Urinary Tract Cell System
- Human Bladder Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Urothelial Cells
- Human Bladder Stromal Fibroblasts
- Human Bladder Fibroblast
Ocular Cell System
- Human Oral Keratinocytes
- Human Gingival Fibroblasts
- Human Gingival Keratinocyte
- Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts
- Human Oral Fibroblasts
Gastrointestinal Cell System
- Human Esophageal Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Esophageal Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Esophageal Epithelial Cells
- Human Esophageal Fibroblasts
- Human Gastric Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Gastric Fibroblasts
- Human Mesenteric Fibroblasts
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Intestinal Fibroblasts
- Human Intestinal Myofibroblasts
- Human Colonic Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Colonic Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Colonic Epithelial Cells
- Human Rectal Fibroblasts
- Human Rectal Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Rectal Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Pancreatic Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Spleen Cell System
- Human Splenic Endothelial Cells
- Human Splenic Fibroblasts
Tonsil Cell System
- Human Tonsil Endothelial Cells
- Human Tonsil Epithelial Cells
- Human Tonsil Fibroblasts
Thyroid Cell System
- Human Thyroid Fibroblasts
Renal Cell System
- Human Renal Glomerular Endothelial Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells
- Human Renal Cortical Epithelial Cells
- Human Renal Epithelial Cells
- Human Renal Mesangial Cells
Pulmonary Cell System
- Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells
- Human Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Pulmonary Artery Adventitial Fibroblasts
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
- Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells
- Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells
- Human Pulmonary Fibroblasts
- Human Bronchial Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Tracheal Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Bronchial Fibroblasts
- Human Tracheal Fibroblasts
- Human Pulmonary Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Endocrine Cell System
- Human Adrenal Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Adrenal Cortical Cells
- Human Adrenal Fibroblasts
- Human Thyroid Fibroblasts
- Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells
- Human Thymic Epithelial Cells
- Human Thymic Fibroblasts
Oral Cell System
- Human Corneal Epithelial Cells
- Human Keratocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Lens Epithelial Cells
- Human Iris Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Conjunctival Fibroblasts
- Human Non-Pigmented Ciliary Epithelial Cells
- Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Human Iris Fibroblasts
- Human Ocular Choroid Fibroblasts
- Human Conjunctival Epithelial Cells
Auditory Cell System
- Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cells
- Human Middle Ear Fibroblast
Hair Cell System
- Human Hair Dermal Papilla Cells
- Human Hair Germinal Matrix Cells
- Human Hair Outer Root Sheath Cells
- Human Hair Inner Root Sheath Cells
- Human Hair Follicular Keratinocytes
- Human Follicle Dermal Papilla Cells
Human Pericytes
- Human Pericytes from Placenta
Macrophages
- Human M1 Macrophages
- Human M2 Macrophages
Male Reproductive Cell System
- Human Prostate Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Bladder Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Prostate Epithelial Cells
- Human Prostate Fibroblasts
- Human Prostate Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Seminal Vesicle Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Seminal Vesicle Epithelial Cells
- Human Testicular Endothelial Cells
- Human Sertoli Cells
Female Reproductive Cell System
- Human Myometrial Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Cervical Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Uterine Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Uterine Fibroblasts
- Human Uterine Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Ovarian Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Mammary Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Mammary Epithelial Cells






Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *