Serological pipettes are essential laboratory instruments designed for precise liquid measurement and transfer in scientific research and clinical settings. We will explore the fundamental structure and components of these pipettes, highlighting their importance in maintaining experimental accuracy and reliability.
The precision and versatility of serological pipettes make them indispensable in modern laboratory work across various scientific disciplines. Understanding the proper usage methods of these pipettes is crucial for laboratory professionals to ensure accurate results and prevent contamination during sensitive procedures.
Key Takeaways
- Serological pipettes are used for precise liquid measurement and transfer.
- They are essential in laboratory settings for scientific research and clinical applications.
- The precision of serological pipettes ensures experimental accuracy and reliability.
- Proper usage methods are crucial to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results.
- Serological pipettes are versatile and used across various scientific disciplines.
Understanding Serological Pipettes
Serological pipettes are a crucial tool in laboratory settings, facilitating precise measurement and transfer of liquids. They are an essential component in various scientific research applications.
What Are Serological Pipettes?
Serological pipettes are designed for accurate liquid handling. They come in different materials, including glass and plastic, each offering unique benefits. The choice of material affects the pipette’s design and overall efficiency in laboratory procedures.
History and Development
The evolution of serological pipettes has been significant, transforming from simple glass instruments to sophisticated tools with advanced design features. Originally, pipettes were made of glass, but with advancements in technology, plastic disposable options became available, enhancing laboratory efficiency and reducing contamination risks.
| Material | Characteristics | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | Durable, resistant to chemicals | Reusable, accurate |
| Plastic | Disposable, cost-effective | Reduces contamination risk, convenient |
Understanding the historical context and development of serological pipettes provides valuable insights into their current design and future advancements in laboratory instrumentation.
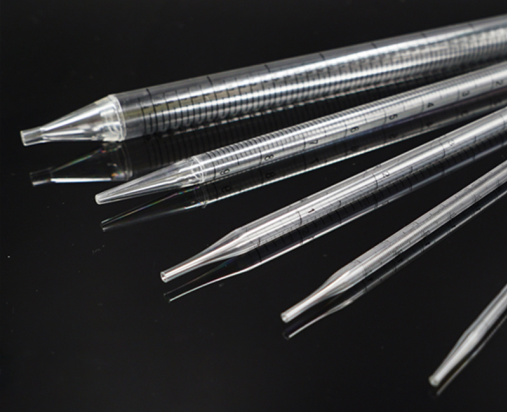

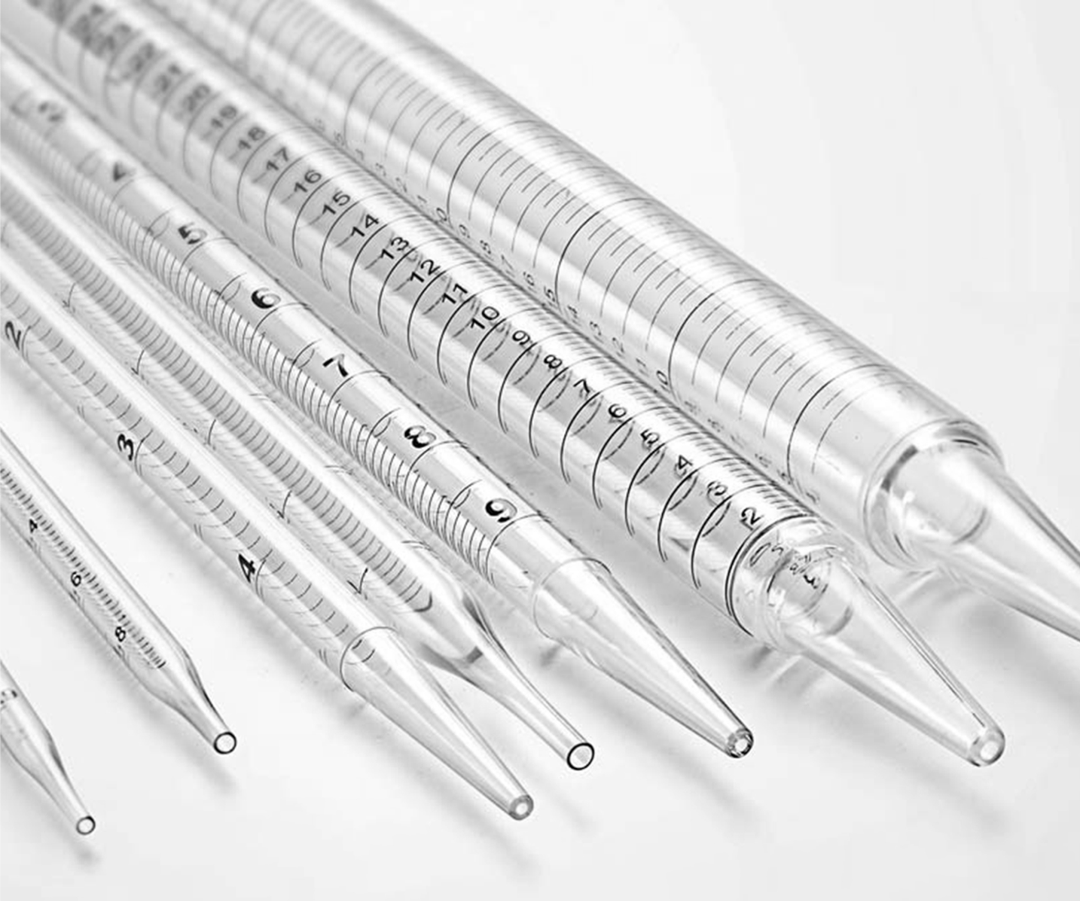
Serological Pipettes Parts img
Serological Pipette Parts and Structure
The anatomy of a serological pipette includes several critical parts that contribute to its overall performance and precision. Understanding these components is essential for laboratory professionals to effectively utilize these tools in various applications.
Main Components of Serological Pipettes
Serological pipettes are composed of several key elements that work together to facilitate accurate liquid handling. The main components include the pipette body, graduated markings, and the tapered tip. The pipette body is the main structure that contains the graduated markings, indicating different volumes of liquid. These markings are calibrated to exacting standards to ensure precision in measurement.
The tapered tip is designed for controlled liquid dispensing, reducing turbulence and ensuring smooth flow during transfer operations. Many modern serological pipettes feature a “reverse graduation” system, where the zero mark is at the tip, allowing for more intuitive measurement when dispensing liquids.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Pipette Body | Contains graduated markings for volume measurement |
| Graduated Markings | Indicate different volumes of liquid |
| Tapered Tip | Facilitates controlled liquid dispensing |
Material Composition
Serological pipettes are typically made from materials that offer durability and resistance to chemicals. The most common materials used are glass and plastic. Glass pipettes are valued for their chemical inertness and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of laboratory applications. On the other hand, plastic pipettes are more cost-effective and disposable, reducing the risk of contamination.
Design Features for Precision
The design of serological pipettes incorporates several features that enhance their precision and performance. The graduated markings are designed to be clear and easy to read, even in varied lighting conditions. The internal diameter of the pipette is carefully engineered to balance capillary action and flow rate, optimizing liquid handling for different viscosities.
Advanced serological pipettes may also feature specialized surface treatments that improve fluid delivery accuracy by reducing surface tension effects and ensuring complete dispensing. These design features collectively contribute to the overall accuracy and reliability of serological pipettes in laboratory settings.

Serological Pipettes details
Types of Serological Pipettes
The classification of serological pipettes into distinct types reflects their adaptability to various laboratory tasks. Serological pipettes are essential tools in laboratories, and their categorization is based on design, material, and functionality.
Open-End Pipettes
Open-end pipettes are designed for applications where the pipette tip is not required to be sterile or where the user needs to dispense liquids directly from the pipette. These pipettes are versatile and can be used for a variety of tasks in the lab. They are typically made from either glass or plastic, offering flexibility in terms of durability and disposability.
Bacteriological Pipettes
Bacteriological pipettes are specifically designed for microbiological applications. They are usually made to be sterile and are used for handling bacteria and other microorganisms. The design of these pipettes minimizes the risk of contamination, making them ideal for sensitive applications.
Aspirating Pipettes
Aspirating pipettes are used for precise liquid handling and are often employed in applications requiring accurate measurement and transfer of liquids. These pipettes are designed to provide consistent performance, making them valuable in laboratory settings.
Differences Between Glass and Plastic Serological Pipettes
Serological pipettes are made from either glass or plastic, each offering distinct advantages. Glass pipettes, constructed from borosilicate glass, provide excellent chemical resistance and durability. Plastic pipettes, made from materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET), offer convenience through their disposable nature, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
| Material | Chemical Resistance | Durability | Disposability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | High | High | No |
| Plastic | Moderate | Low | Yes |
Understanding the differences between glass and plastic serological pipettes is crucial for selecting the appropriate type for specific laboratory applications. The choice between glass and plastic pipettes depends on factors such as the required chemical resistance, durability, and the need for disposability.

Serological Pipettes Parts
Proper Usage Methods of Serological Pipettes
To achieve accurate results in laboratory settings, understanding the proper usage of serological pipettes is crucial. We will guide you through the step-by-step operating procedure, best practices for accuracy, and common errors to avoid when using these essential laboratory tools.
Step-by-Step Operating Procedure
To ensure accurate measurements, follow these steps when using serological pipettes. First, select the appropriate pipette for your task, considering factors such as volume and tip type. Next, pre-wet the pipette tip by aspirating and dispensing the liquid once before taking your measurement. When aspirating, immerse the tip to the correct depth, avoiding contact with the container bottom to prevent contamination. Aspirate the liquid slowly and steadily to prevent turbulence, which can affect measurement accuracy. After dispensing the liquid, ensure all fluid has drained from the pipette tip before removing it from the vessel. If using a blow-out pipette, indicated by two rings at the top, press down on the controller again to expel any remaining liquid.
Best Practices for Accuracy
To maintain accuracy when using serological pipettes, adhere to best practices. Always maintain eye level with the liquid surface when reading the meniscus to avoid parallax errors. Use consistent lighting conditions to ensure accurate volume readings. Additionally, handle the pipette and tips with care to prevent contamination and damage. Regularly calibrate your pipettes to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Common errors when using serological pipettes include inconsistent meniscus reading, improper immersion depth of the pipette tip, and failure to pre-wet the pipette. To avoid these errors, maintain a steady hand, follow proper aspiration techniques, and pre-wet the pipette tip before measurement. Be aware of the potential for contamination and take steps to minimize it by handling the pipette and tips carefully. By following these guidelines and being mindful of the potential pitfalls, you can ensure accurate and reliable results when using serological pipettes.
Applications of Serological Pipettes in Laboratory Settings
Serological pipettes play a crucial role in various laboratory settings due to their precision and versatility. These pipettes are used in a wide range of applications, from cell culture to clinical diagnostics.
Cell Culture Applications
In cell culture, serological pipettes are used for handling cell suspensions, media, and reagents. Their accuracy ensures that the right amounts are dispensed, which is critical for maintaining healthy cell cultures. You can rely on these pipettes for precise measurements, which is essential for the success of cell culture experiments.
Microbiology and Serology Uses
Serological pipettes are essential in microbiology and serology for preparing cultures, diluting samples, and handling sera. The precision of these pipettes is vital for obtaining accurate results in diagnostic tests and research. We use them to ensure that samples are prepared consistently and accurately.
Chemical Analysis and Research Applications
In chemical analysis and research, serological pipettes are used for preparing standards, calibrators, and samples for various analytical techniques. Their accuracy and reliability are crucial for the validity of the analysis. You will find that these pipettes are indispensable for achieving precise results in your research.
Clinical Laboratory Applications
Clinical laboratories rely on serological pipettes for a variety of diagnostic procedures, including preparing patient samples for analysis. The sterile and disposable nature of modern serological pipettes supports safety protocols, preventing cross-contamination between patient samples. With a wide range of volumes available, these pipettes accommodate diverse measurement needs in diagnostic testing.
Overall, serological pipettes are a fundamental tool in laboratory settings, offering the precision and versatility needed for a wide range of applications. Their use ensures accuracy, reliability, and safety in various laboratory procedures.
Accessories and Supporting Equipment
To maximize the effectiveness of serological pipettes, laboratories rely on a range of accessories and supporting equipment.
Pipette Controllers and Fillers
Pipette controllers and fillers are essential for precise handling of serological pipettes. These devices enable accurate aspiration and dispensing of fluids, minimizing the risk of contamination. We recommend using pipette controllers with hydrophobic membrane filters to prevent liquid and aerosol contamination.
Storage Solutions and Stands
Proper storage of serological pipettes is crucial for maintaining their integrity. Storage solutions and stands help keep pipettes organized and within reach, reducing the risk of damage or contamination. Our 1mL Pipet Support ensures that smaller pipettes are held securely.
Filters and Adapters
Filters and adapters play a critical role in enhancing the functionality and safety of serological pipettes. Filters prevent aerosol or liquid cross-contamination, while adapters ensure secure connections between pipettes and controllers. We offer autoclavable silicone adapters and hydrophobic membrane filters to support aseptic techniques.
Conclusion: Importance of Serological Pipettes in Modern Laboratory Work
Serological pipettes remain fundamental instruments in laboratory work, facilitating accurate experiments and research across various scientific disciplines.
Their precise liquid handling capabilities support advancements in cell culture, microbiology, and chemical analysis, making them indispensable in modern laboratory settings.
The evolution of serological pipettes from simple glass tubes to sophisticated measurement tools reflects the increasing demands for precision and reproducibility in scientific research.
With the availability of both reusable glass and disposable plastic pipettes, laboratories can choose options that balance environmental considerations, budget constraints, and specific applications requirements.
Modern pipettes are supported by accessories like electronic controllers, which enhance ergonomics and productivity while reducing user fatigue.
Understanding the structure, proper usage techniques, and maintenance requirements of serological pipettes is essential for laboratory professionals seeking to optimize their experimental procedures and improve overall productivity.
As laboratory techniques continue to advance, pipettes adapt through innovations in materials and design features, ensuring their continued relevance in scientific research and applications.
References and further readings:
1.Batchelor, H., & Marriott, J. (2014). Aseptic laboratory techniques: Volume transfers with serological pipettes and micropipettors. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (84), e3941987.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3941987/
2.Collins, S. R. (2015). Basic serologic laboratory techniques. In Clinical Laboratory Science: The Basics and Routine Techniques (6th ed.). Clinical Gate.
https://www2.hawaii.edu/~johnb/micro/m140/syllabus/week/handouts/m140.2.3.htm
3.Bishop, J. (n.d.). Biotechnology laboratory manual: Serological pipettes. University of Hawaii Microbiology Department. https://www2.hawaii.edu/~johnb/micro/m140/syllabus/week/handouts/m140.2.3.htm
FAQ
What is the purpose of using a pipette in laboratory settings?
We use pipettes to accurately measure and transfer small volumes of liquid, ensuring precision and minimizing contamination in various laboratory applications, including cell culture and microbiology.
How do I choose the right type of pipette for my laboratory needs?
You can select the appropriate pipette based on factors such as the type of liquid being handled, the required volume range, and the desired level of precision. We offer various types of pipettes, including glass and plastic options, to suit different laboratory applications.
What are the best practices for maintaining pipette accuracy?
To ensure pipette accuracy, we recommend regular calibration, proper handling, and storage in a dry, clean environment. You should also follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance and use.
Can I use pipettes for handling hazardous materials?
Yes, you can use pipettes for handling hazardous materials, but it’s essential to take necessary safety precautions, such as wearing protective gloves and using pipette tips with filters to prevent contamination and exposure.
How do I prevent contamination when using pipettes?
To minimize contamination, we suggest using sterile pipette tips, handling pipettes carefully, and avoiding cross-contamination by using separate pipettes for different samples and reagents.
What are the differences between manual and automated pipettes?
Manual pipettes require manual operation, while automated pipettes use electronic controls for more precise and efficient liquid handling. You can choose between these options based on your laboratory’s specific needs and workflow.
How do I properly store pipettes and their accessories?
You should store pipettes in a dry, clean environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. We recommend using pipette stands and storage solutions to keep pipettes organized and within easy reach.
Leo Bios
Hello, I’m Leo Bios. As an assistant lecturer, I teach cellular and
molecular biology to undergraduates at a regional US Midwest university. I started as a research tech in
a biotech startup over a decade ago, working on molecular diagnostic tools. This practical experience
fuels my teaching and writing, keeping me engaged in biology’s evolution.









Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *