Are you ready to unlock the mysteries hidden within human blood cells? The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are a fascinating gateway. They help us understand complex immunological processes and groundbreaking medical research.
The PBMC separation protocol is a key technique in biomedical research. It allows scientists to isolate and study white blood cells. These cells, including lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells, are vital for our immune system’s function and disease response.
Researchers using the PBMC separation protocol can extract about 55% of total blood volume. They focus on cells with round nuclei, which are crucial for immunological investigations. By using advanced techniques like density gradient centrifugation, scientists can isolate cells with great accuracy.
Key Takeaways
- PBMC separation is fundamental for advanced immunological research
- Standard isolation methods require specialized centrifugation techniques
- Proper cell handling ensures high-quality research outcomes
- PBMCs represent diverse immune cell populations
- Modern isolation techniques continue to improve cell recovery efficiency
Introduction to PBMC Separation
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are key in biomedical research. They help us understand how our bodies fight off infections. These cells are vital for many studies, from how our immune system works to testing new medicines.
Separating blood cells is a complex task. Density gradient centrifugation is a main method for getting these important cells from blood samples.
Understanding PBMC Composition
PBMCs include several important cell types for our immune system:
- Lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
- Monocytes
- Macrophages
Significance in Scientific Research
Scientists use PBMCs for many things, like:
- Flow cytometry analysis
- Cell culture experiments
- Immunological studies
- Drug development research
| Cell Type | Percentage in PBMCs | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| T Lymphocytes | 70-80% | Cellular Immunity |
| B Lymphocytes | 10-15% | Antibody Production |
| Monocytes | 10% | Inflammation Response |
Density gradient centrifugation is a good way to separate these cells. It separates blood components by density. This helps scientists get the pure PBMC samples they need for their research.
Overview of the PBMC Separation Protocol
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) isolation is key in biomedical research. It needs precision and careful technique. Researchers use special methods to get these important immune cells from whole blood.
The main goal is to get a clean and alive cell group for science. There are two main ways to do this:
- Density Gradient Centrifugation
- Immunomagnetic Separation
- Microbubble Technology
Density Gradient Centrifugation Methods
Density gradient centrifugation is the top choice for PBMC isolation. Researchers often use ficoll-paque and lymphoprep media. This method uses the different densities of blood cells.
“The success of PBMC isolation depends on precise technique and appropriate separation media.”
Isolation Technique Comparison
| Technique | Purity | Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density Gradient (Ficoll-Paque) | 90-95% | 45-60 minutes | Low |
| Lymphoprep Method | 92-97% | 30-45 minutes | Medium |
| Magnetic Separation | 95-99% | 30 minutes | High |
New methods like microbubble technology are becoming popular. They offer fast and gentle cell separation. The right method depends on the research needs, resources, and cell purity goals.
Key Isolation Considerations
- Keep cell viability above 90%
- Reduce cell damage during separation
- Ensure high-purity cell populations
- Choose technique based on research goals
Materials and Equipment Needed
Getting lymphocytes right needs the right tools and materials. Scientists must gather everything needed for cell separation. This ensures the cells stay healthy and the samples are good.
Essential Reagents for Cell Separation
- Density gradient media (Lymphoprep™ or Ficoll-Paque™)
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS)
- Cell culture medium
- Sterile pipettes and tips
Laboratory Equipment Requirements
Lab tools are vital for getting lymphocytes. Make sure you have these:
- Microbiological safety cabinet
- Centrifuge with swing-out rotor
- Refrigerated centrifuge
- Pipette set with various volume ranges
- Cell counting device
Recommended Centrifugation Parameters
For the best cell separation, follow these steps:
- Centrifugation force: 800 x g
- Duration: 20-30 minutes
- Temperature range: 15-25°C
Choosing the right tube size is key for PBMCS isolation. Good preparation and quality materials are essential for great research.
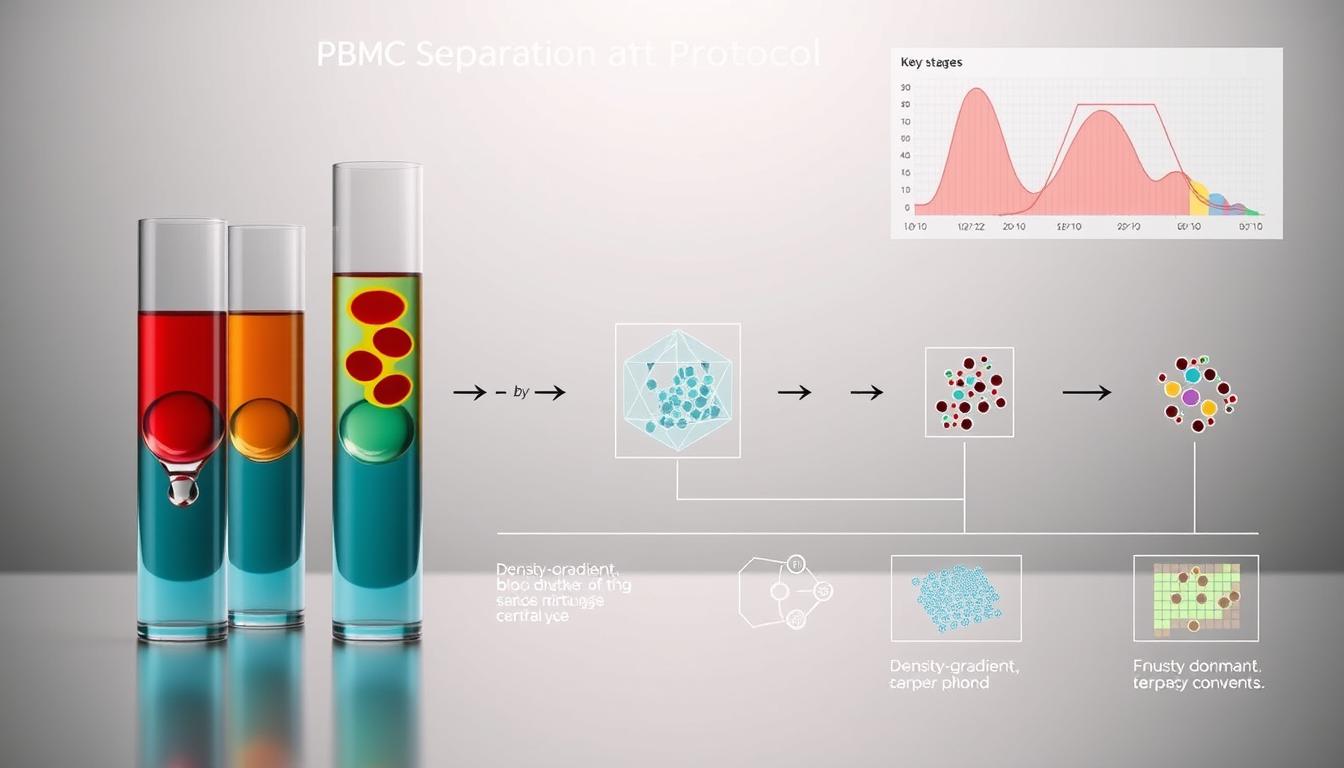
Step-by-Step Protocol for PBMC Separation
Getting precise is key when purifying mononuclear cells. The density gradient centrifugation method is a trusted way to get peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from whole blood.
Preparing the Sample
Before starting, there are important steps to follow:
- Collect fresh blood in the right tubes
- Mix blood with culture medium at a 1:1 ratio
- Make sure all reagents are at room temperature (15-25°C)
- Keep everything sterile
Density Gradient Centrifugation Process
The heart of the process is layering the blood over a density gradient medium like Ficoll-Paque™. It has a density of 1.077 g/ml.
- Add 4 ml of density gradient medium to the tube
- Slowly add the diluted blood (up to 5 ml) on top
- Spin at 400 g for 30 minutes at room temperature
- Look for the clear separation of cell layers
Washing Steps and Cell Recovery
After spinning, use a pipette to carefully take out the mononuclear cell layer. Then, follow these washing steps for top-notch cell prep:
- Move the cell layer to a clean tube
- Mix with 8 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
- Spin at 400 g for 5 minutes
- Resuspend in 2 ml of PBS
The cells should now be 3-4 million per milliliter, ready for your research.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Researchers often face challenges when isolating PBMCs through density gradient centrifugation. Knowing how to tackle these problems can greatly enhance cell recovery and the success of experiments.
Low Cell Yield Challenges
Several factors can lead to low PBMC yield. Important things to consider include:
- Improper blood collection techniques
- Delayed processing beyond recommended timeframes
- Incorrect centrifugation parameters
The best time to process PBMCs is within 8 hours from collection. Blood collected less than 24 hours before separation works best for density gradient procedures.
Contamination Management
Granulocyte contamination can greatly affect experimental results. Studies show that leukopaks usually have 3-10% granulocytes.
| Contamination Factor | Impact | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Red Blood Cell Presence | Reduces PBMC purity | Additional washing steps |
| Granulocyte Contamination | Decreases T cell proliferation | Optimize separation protocol |
Cell Viability Preservation
Keeping cells alive is key in the PBMC separation process. Important factors include:
- Using fresh blood samples
- Maintaining proper temperature (15-30°C)
- Avoiding prolonged DMSO exposure
After thawing, PBMC viability can drop by 10-15%, with an average of 86%. Proper handling during density gradient centrifugation is crucial for the best cell recovery and experimental success.
Best Practices for PBMC Handling
Handling peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) right is key to keeping them alive and useful for research. It’s important to follow certain steps to get the best cell separation technique for these important immune cells.
Optimal Storage Strategies
Cryopreservation is the best way to store PBMCs for a long time. Here are some important things to remember:
- Freeze cells slowly at 1 °C per minute
- Use a cryopreservation solution with 90% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) and 10% DMSO
- Store cryovials at -70/-80 °C
- Ship on dry ice within 4 weeks of preservation
Recommended Cell Culture Techniques
Keeping peripheral blood mononuclear cells alive needs careful attention. Viability expectations should exceed 95%. It’s important to watch the cell concentration and how they are handled.
| Parameter | Recommended Condition |
|---|---|
| Centrifugation Speed | 400 x g for 30 minutes |
| Temperature Range | 15 °C to 30 °C |
| Cell Count Accuracy | ± 15% between quadrants |
Researchers should write down all steps they take. They should also watch out for problems like contamination or mistakes in counting. Choosing the right cell separation technique is crucial for the quality and function of isolated PBMCs.
Applications of Isolated PBMCs
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are key in biomedical research. They help scientists study the immune system in detail. This is done through precise leukocyte separation techniques.
Researchers use PBMCs in many fields. They help us understand how the immune system works. This knowledge is used to create new medical treatments.
Immunology Research Applications
In immunology, PBMCs are vital. They let scientists study how cells fight off infections. Key areas include:
- Analyzing lymphocyte isolation mechanisms
- Studying immune cell functionality
- Investigating cytokine production patterns
- Examining pathogen response mechanisms
Drug Development and Testing
Pharmaceutical researchers use PBMCs a lot. They help find out how drugs work in the body. This is done by:
- Evaluating immune system interactions
- Assessing potential treatment responses
- Screening novel immunomodulatory compounds
PBMCs are also key in personalized medicine. They help scientists understand how each person’s immune system works. This leads to targeted therapeutic strategies.
Safety Considerations
Keeping safe during PBMC isolation is key for researchers and the integrity of experiments. Lab workers must stick to strict biosafety rules when dealing with biological samples.
Working with human blood samples means following strict safety rules. The whole PBMC processing needs careful attention to safety.
Biosafety Laboratory Requirements
PBMC isolation must happen in a Biosafety Level 2 (BSL-2) lab. This special place offers vital protection against biological dangers.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) at all times
- Wear double-layer non-latex gloves
- Use disposable arm sleeves
- Always work inside a Class II Biosafety Cabinet
Safe Handling of Density Gradient Media
When using density gradient media like ficoll-paque and lymphoprep, follow these steps:
- Handle media in a controlled, sterile environment
- Wear appropriate protective eyewear
- Use chemical-resistant gloves
- Avoid direct skin contact with gradient solutions
Proper decontamination and disposal of potentially infectious materials are crucial. Always follow guidelines for managing biological samples.
Safety is not an option—it’s a requirement in biological research.
Conclusion and Further Reading
The field of mononuclear cell purification is growing fast. It offers new ways to extract buffy coat and isolate PBMCs. This helps scientists in biomedical research get important insights into many areas.
Studies show that PBMCs have a lot of potential. They can be recovered up to 88% and separated with about 85% efficiency. It’s important for researchers to pay close attention to the details of their work.
Key Takeaways for Researchers
Doing good PBMC research means being very careful from start to finish. It’s key to keep the cells alive and use the right activation methods. Using the same steps every time helps reduce mistakes and makes the cells more useful.
Recommended Resources
Researchers should keep learning by reading special immunology journals and going to cell biology conferences. Joining professional groups focused on cell purification is also a good idea. This way, they can stay up-to-date with new discoveries and improve their work.
FAQ
What are Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)?
PBMCs are a type of white blood cells. They include lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells. These cells are key to our immune system. They are isolated from whole blood using special techniques.
Why are PBMCs important in research?
PBMCs are crucial in many research areas. They help us understand the immune system and how it works. They also aid in drug development and personalized medicine.
What is the most common method for PBMC isolation?
The most common method is density gradient centrifugation. This uses media like Ficoll-Paque to separate cells based on density.
How long can isolated PBMCs be stored?
PBMCs can be stored for 24-48 hours at 4°C. For longer storage, they can be frozen in liquid nitrogen. Specialized freezing media is needed to keep cells alive and functional.
What are the main challenges in PBMC separation?
Challenges include low cell yield and contamination. Proper technique and protocols can help overcome these issues.
What safety precautions are necessary when working with PBMCs?
Safety measures include wearing PPE and working in a biosafety cabinet. Proper handling and disposal of biological samples are also important.
Can PBMCs be used for multiple research applications?
Yes, PBMCs are versatile. They can be used in immunophenotyping, cytokine analysis, and more.
What factors affect PBMC quality during isolation?
Factors include blood collection method and processing time. Maintaining sterile conditions is crucial for cell viability.
How can researchers improve PBMC isolation efficiency?
Improving efficiency involves using high-quality media and optimizing centrifugation. Following standardized protocols is also key.
Are there alternatives to density gradient centrifugation for PBMC isolation?
Yes, alternatives include MACS, FACS, and commercial kits. These offer faster and less labor-intensive methods.









Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *