Ever thought about how scientists and brewers turn simple stuff into complex, valuable things? The role of a fermenter is more fascinating than you might think.
Fermenters are advanced containers that help create the best conditions for microbes to grow and make products. They are key in many fields, from making food to finding new medicines.
The fermentation process is all about controlling conditions so microbes can turn raw materials into what we need. People in research and industry use fermenters to control things like temperature, pH, and nutrients very carefully.
Fermenters come in all sizes, from small ones for home brewing to huge tanks for big industries. Their ability to adapt makes them crucial for science and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Fermenters create controlled environments for microbial growth
- They support critical biological transformation processes
- Sizes range from 1 gallon to thousands of gallons
- Used across multiple industries including food, pharmaceuticals, and research
- Enable precise management of biological conditions
Understanding Fermentation
Fermentation is a cool biological process that changes organic stuff into simpler things. It uses tiny living things to break down big compounds. This makes new products through yeast fermentation and anaerobic digestion.
For a long time, scientists have seen fermentation as a key way for life to make energy without air. It’s all about microbes turning carbs into acids, gases, or alcohols through special chemical reactions.
Defining the Fermentation Process
Fermentation has a few main points:
- It changes carbs without using oxygen
- It makes energy through tiny life forms
- It creates special chemical stuff
- It can happen in many places
Historical Exploration of Fermentation
Fermentation has been around for thousands of years. Old civilizations used it to keep food fresh and make drinks. Yeast fermentation helped make bread, wine, and beer.
“Fermentation is not just a process, but a testament to the ingenuity of biological systems.” – Scientific Fermentation Research Group
| Fermentation Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Organisms |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic Fermentation | Produces ethanol and CO2 | Yeast |
| Lactic Acid Fermentation | Creates lactic acid without oxygen | Bacteria |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Breaks down organic matter | Mixed microbial populations |
Today, we know more about fermentation. It’s key in biotech, food, and industry. Scientists are still learning about anaerobic digestion. They hope it will change how we get energy and food.
The Role of Fermenters in Biotechnology
Biotechnology has changed how we make things by using microbes. Fermenters, or bioreactors, are key in turning microbes into tools for many industries.

Today, fermenters help make many important products. They let scientists control how microbes work. This makes production more efficient.
Key Applications in Industry
Fermenters are vital in several areas:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Food and Beverage Production
- Biofuel Generation
- Enzyme and Protein Development
“Fermentation technology represents a transformative approach to industrial production, enabling unprecedented precision and scalability.” – Biotechnology Research Institute
Types of Fermenters Used
There are different fermenters for different needs. Each has its own benefits for making products:
| Fermenter Type | Primary Application | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Fermenters | Research and Small-Scale Production | Closed system, limited volume |
| Continuous Fermenters | Large-Scale Industrial Production | Constant nutrient supply, steady output |
| Fed-Batch Fermenters | Complex Biochemical Processes | Controlled nutrient addition, high yield |
Choosing the right bioreactor depends on what you need to make. New fermentation methods are always improving what we can do in biotech.
Main Functions of a Fermenter
Fermenters are key in biotechnology and industry. They help grow microbes and make useful products. Knowing how fermenters work shows their big role in science and business.
Fermenters do two main things: make products and help cells grow. They make a good place for microbes to live and work. This lets them make important things through fermentation.
Production of Metabolites
Fermenters make many products by controlling the environment. Important things for making products include:
- Precise temperature control
- Optimal pH regulation
- Nutrient supply management
- Oxygen and gas exchange monitoring
“Fermentation is not just a process, but a delicate art of creating conditions where microorganisms can transform raw materials into valuable products.” – Biotechnology Research Institute
Cell Growth and Maintenance
Biomass conversion needs the right place for microbes to grow. Fermenters help with this by:
- Controlled nutrient introduction
- Consistent environmental parameters
- Effective mixing and aeration
- Protection from contamination
| Fermentation Parameter | Optimal Range | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 15-25°C | Influences metabolite yield |
| pH Level | 3.0-4.0 | Determines microbial growth |
| Oxygen Management | Staged Introduction | Supports cell reproduction |
By controlling these things, fermenters help make more products. They also make sure the biomass conversion is good in many uses.
Components of a Fermenter
A bioreactor is a complex system with many parts. Each part is vital for creating the right environment for microbes to grow and produce metabolites.
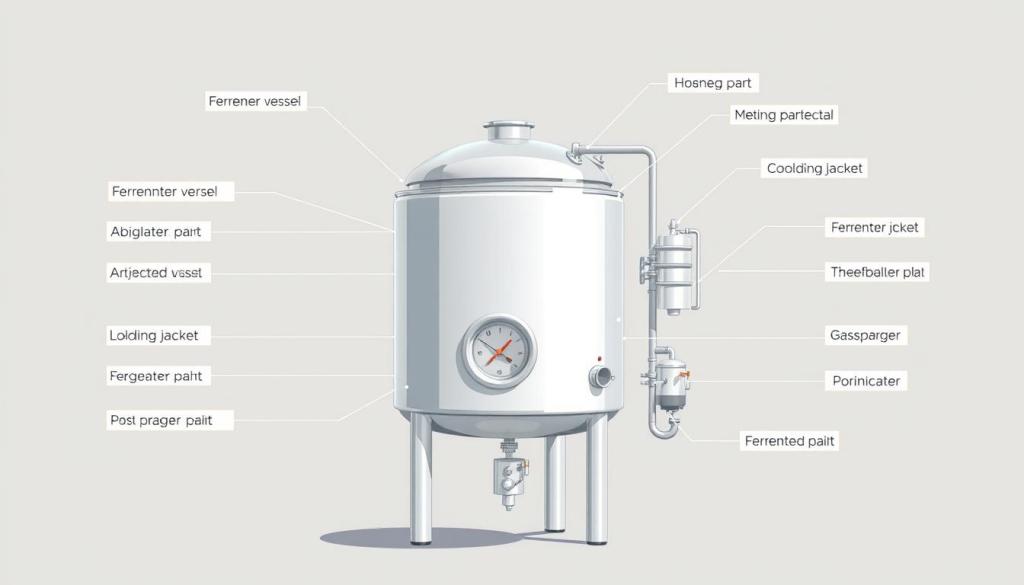
The key parts of a fermenter help control and monitor the fermentation process.
Essential Parts and Their Critical Functions
- Fermenter Vessel: The main container for the fermentation medium
- Agitation System: Makes sure everything mixes well and gets enough oxygen
- Aeration Mechanism: Adds oxygen for the microbes to use
- Temperature Control System: Keeps the right temperature for growth
- pH Monitoring Equipment: Watches and adjusts the acidity levels
Sterilization: Protecting the Fermentation Environment
Sterilization is key in bioreactor work. It keeps the environment clean and free from contaminants, ensuring the product’s quality.
“In fermentation, sterility is not just a preference—it’s a necessity for successful microbial cultivation.”
| Component | Primary Function | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Vessel | Contain fermentation medium | Material resistance to corrosion |
| Agitator | Ensure uniform mixing | Impeller design impacts efficiency |
| Sparger | Introduce oxygen | Bubble size affects gas transfer |
| Temperature Control | Maintain optimal growth conditions | Precise heating/cooling systems |
Today’s fermenters use the latest technology for complex biotech processes. They ensure consistent results and high-quality products in many industries.
Types of Fermenters
Bioreactors are key in microbial fermentation, with various designs for different needs. Knowing the types of fermenters helps in improving production in many fields.
Fermentation technologies have grown to meet specific needs. This has led to three main types of fermenters:
Batch Fermenters
Batch fermenters are the simplest design. They grow microorganisms in a closed space for a set time. They are known for:
- Limited production volume
- Precise control over initial conditions
- Ideal for small-scale and research applications
Continuous Fermenters
Continuous fermentation is a dynamic way to grow microorganisms. These bioreactors keep nutrients flowing in and waste out, for ongoing production.
- Steady nutrient input and waste removal
- Consistent microorganism growth
- Suited for large-scale industrial processes
Fed-Batch Fermenters
Fed-batch fermenters mix batch and continuous systems. They add nutrients during fermentation, improving microbial metabolism.
- Incremental nutrient supplementation
- Enhanced product yield
- Flexibility in process management
“The right fermenter design can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality in microbial fermentation.” – Biotechnology Research Institute
Choosing the right fermenter depends on what you want to produce, the microorganism, and the desired outcome.
Fermentation Process Overview
The fermentation process is key to making many important products in different fields. It shows how tiny organisms change raw stuff into useful things.
Fermentation has many steps that change organic stuff through tiny life forms. These steps help turn things into something new.
Fundamental Steps in the Fermentation Process
- Media Preparation: Creating the best nutrient mix
- Inoculation: Adding the right tiny life forms
- Active Fermentation: Starting the chemical reactions
- Product Recovery: Getting the wanted stuff
Key Factors Influencing Yeast Fermentation
Yeast fermentation needs the right conditions to work well. These conditions affect how well the yeast works and the quality of what it makes.
| Parameter | Impact on Fermentation |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Controls how fast the yeast works |
| pH Levels | Changes how enzymes work and how well the yeast grows |
| Oxygen Availability | Changes how the yeast breaks down food |
| Nutrient Composition | Helps the yeast grow and make products |
It’s interesting that over 25% of bacteria and archaea can ferment. This shows how common this process is. During fermentation, tiny life forms make 2 to 4.5 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule. This shows how efficient this process is.
The beauty of fermentation lies in its ability to transform simple ingredients into complex, valuable products through microbial alchemy.
Fermentation is very important in many industries, like food and biofuels. Knowing how it works helps scientists make things better and find new ways to do things.
Monitoring and Controlling Fermentation
Monitoring and controlling fermentation is key. It’s all about keeping the environment just right. This is true for many industries.
Bioreactors need constant checks on important factors. These factors affect how microbes grow and the quality of products. To get the best results, advanced monitoring is a must.
Importance of Environmental Conditions
Controlling the environment is crucial for fermentation success. Important things to manage include:
- Temperature stability
- pH level maintenance
- Dissolved oxygen concentration
- Nutrient availability
“Precision in environmental control is the cornerstone of successful fermentation processes.” – Biotechnology Research Institute
Techniques for Monitoring
Today’s fermentation control uses advanced tech. It tracks key parameters in real-time. The methods include:
- Online sensor systems
- Spectroscopic analysis
- Digital data logging
- Automated feedback mechanisms
Monitoring fermentation involves collecting vital data. Real-time tracking lets researchers make quick changes. This ensures product quality and boosts yield.
New bioreactor tech has advanced sensors. These sensors catch even small changes in fermentation. This gives better control and optimization.
Advantages of Using Fermenters
Fermenters are key in modern biotechnology, changing many industries. They make production better, especially in making ethanol and turning biomass into useful products.
Using fermenters brings big wins over old ways of making things. They make production faster and more flexible in making biochemicals.
Increased Yield and Efficiency
Fermenters help make more product by controlling the environment. The main benefits are:
- Optimized nutrient delivery
- Precise temperature regulation
- Controlled pH management
- Enhanced microbial growth conditions
In making ethanol, fermenters boost conversion rates. Some systems get up to 95% efficiency in biomass conversion.
Versatility in Applications
Fermenters work well in many fields, showing their great potential:
| Industry | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Biofuels | Ethanol Production | High conversion efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Enzyme Manufacturing | Precise biochemical synthesis |
| Food Processing | Fermented Product Development | Consistent quality control |
“Fermenters are not just machines; they are the future of sustainable and efficient biochemical production.” – Biotechnology Research Institute
Advanced fermenter tech keeps growing, offering green solutions for industries.
Fermenters in Food Production
Fermentation is key in making tasty food and drinks. It turns simple ingredients into delicious products. This ancient method is still used today in many parts of the world.
Role in Brewing and Winemaking
Beer brewing and wine making are top examples of fermentation. They turn basic ingredients into tasty drinks. This is done through careful control of microbes.
- Beer brewing changes grain starches into sugars that can be fermented.
- Wine making uses yeast to turn grape sugars into alcohol.
- Fermenters help control temperature and microbial activity.
Beer brewing is over 13,000 years old, with the first evidence found in Israel. Winemaking started around 6000 BC in Georgia. These show fermentation’s long history.
Fermentation in Dairy Products
Dairy fermentation turns milk into things like yogurt and cheese. Special bacteria are used to create these products. They add unique flavors and textures.
| Dairy Product | Fermentation Characteristics | Key Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Yogurt | Milk protein denaturation | Lactobacillus, Streptococcus |
| Swiss Cheese | Propionic acid production | Propionibacterium |
Fermentation not only preserves food but also enhances nutritional value and creates distinctive flavors.
Today, fermentation technology is getting better. It makes food products more efficiently and precisely. This shows how humans have always been creative in making food.
Future Trends in Fermentation Technology
Fermentation technology is changing fast, thanks to new discoveries in microbial fermentation and biotechnology. Scientists are exploring new ways to make things, like genetic engineering and synthetic biology. These methods help create microbes that can make complex things more efficiently.
New technologies are making anaerobic digestion better, like microfluidic bioreactors. These systems let scientists control and study microbial growth in detail. They also use next-generation sequencing to understand microbes better.
Fermentation is not just for food anymore. It’s being used for things like bioplastics, biofuels, and even meat. CRISPR technology is helping scientists make microbes better, opening up new uses for fermentation.
Experts think fermentation will keep getting better, with a focus on being more efficient and green. The mix of biotechnology, genetic engineering, and monitoring systems will lead to big changes. This could change how we make food, drugs, and solve environmental problems.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a fermenter?
Fermenters create the best environment for microbes to grow and make products. They control things like temperature, pH, and nutrients. This helps in making medicines, food, and biofuels.
How do fermenters differ from traditional production methods?
Fermenters control biological processes better than old methods. They help make products more efficiently and accurately. This is because they can change conditions in real time.
What types of products can be produced using fermenters?
Fermenters make many things like medicines, enzymes, and biofuels. They also make drinks and organic acids. They’re key in biotech for making complex molecules.
What are the main types of fermentation systems?
There are batch, continuous, and fed-batch fermenters. Batch ones use one batch of substrate. Continuous ones keep the flow steady. Fed-batch adds nutrients during the process.
How important is sterilization in fermenter operations?
Sterilization is very important to keep fermenters clean. It stops unwanted microbes from ruining the process. This keeps the product safe and pure.
What industries most extensively use fermentation technology?
Many industries use fermentation. These include pharmaceuticals, food, biofuels, and chemicals. It’s used in brewing, making cheese, and making antibiotics.
How do modern fermenters monitor and control processes?
Modern fermenters use sensors and computers to watch important things. They adjust conditions like temperature and pH in real time. This helps microbes grow well and make products.
What role does biotechnology play in fermenter development?
Biotech is changing fermenters with genetic engineering and synthetic biology. It makes microbes better and lets us make more things. This makes fermentation more efficient.
Are fermenters environmentally sustainable?
Yes, fermenters are good for the environment. They use green resources and make less waste. They help make clean energy like biofuels.
What are emerging trends in fermenter technology?
New trends include smaller bioreactors and better control systems. There’s also high-throughput screening and new uses like cultured meat. These are changing how we use fermenters.









Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *